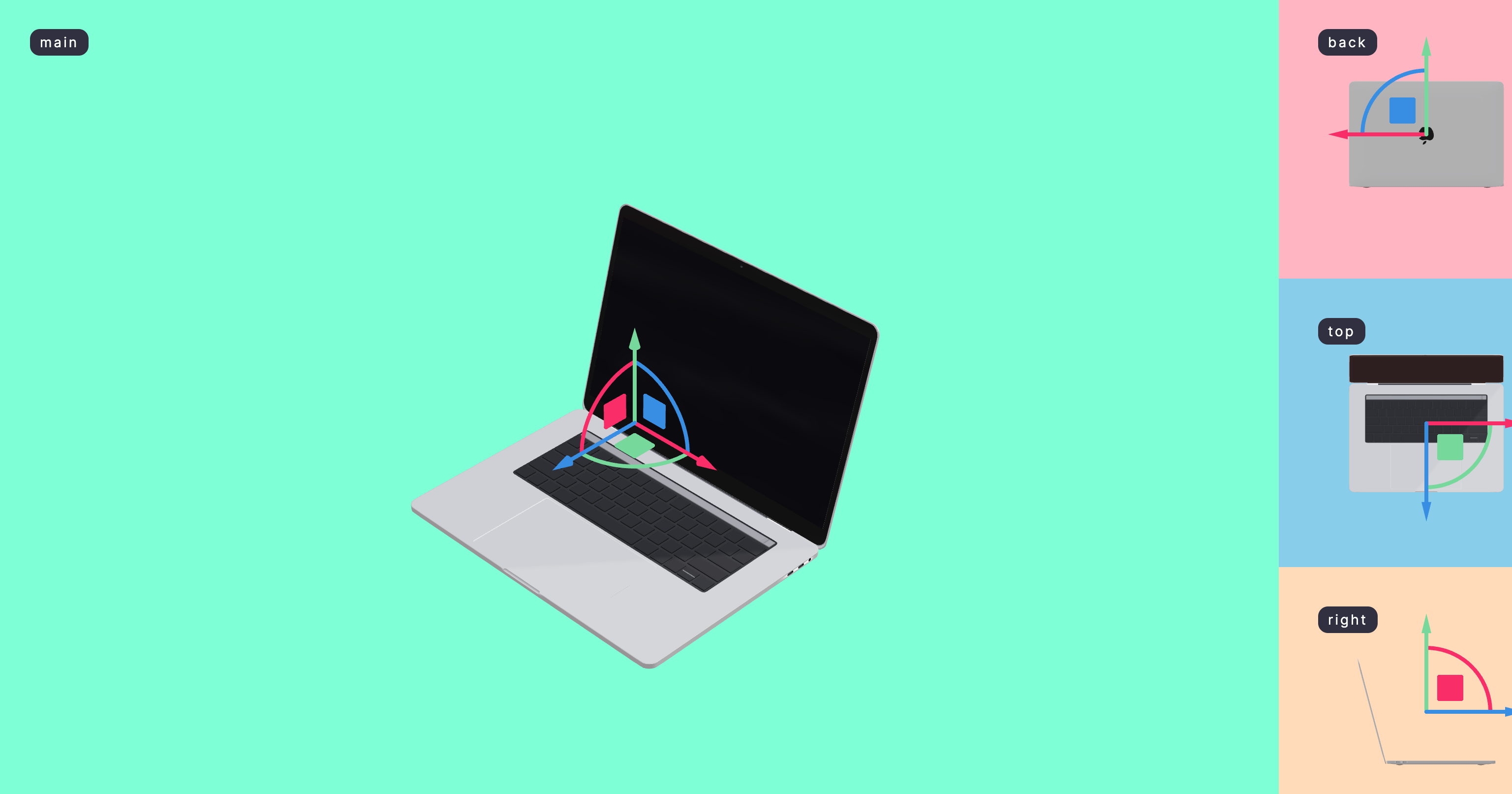
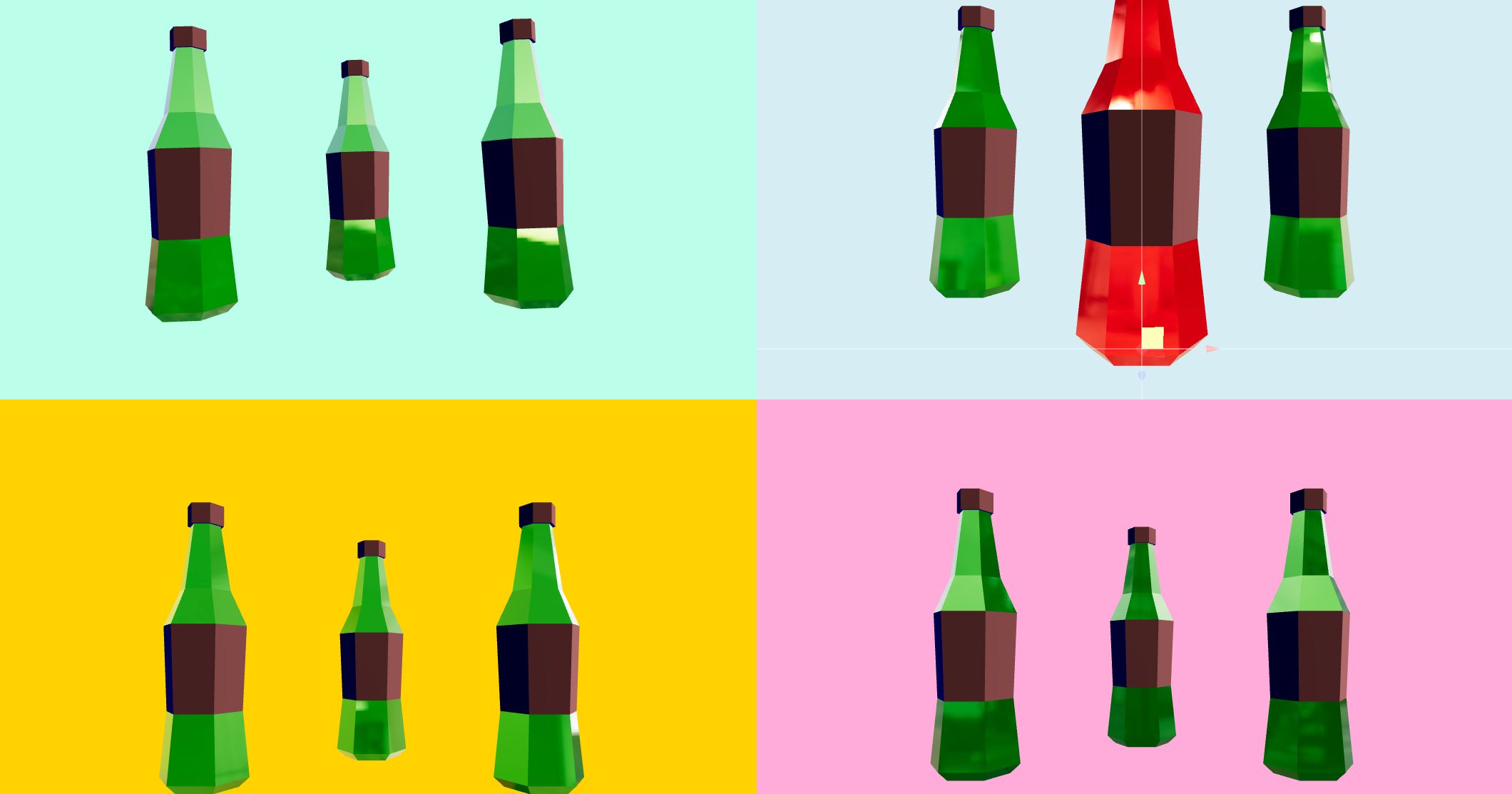
View
Views use gl.scissor to cut the viewport into segments. You tie a view to a tracking div which then controls the position and bounds of the viewport. This allows you to have multiple views with a single, performant canvas. These views will follow their tracking elements, scroll along, resize, etc.
It is advisable to re-connect the event system to a parent that contains both the canvas and the html content. This ensures that both are accessible/selectable and even allows you to mount controls or other deeper integrations into your view.
Note that
@react-three/fibernewer than^8.1.0is required forViewto work correctly if the canvas/react three fiber root is not fullscreen. A warning will be logged if drei is used with older versions of@react-three/fiber.
export type ViewProps = {
/** Root element type, default: div */
as?: string
/** CSS id prop */
id?: string
/** CSS classname prop */
className?: string
/** CSS style prop */
style?: React.CSSProperties
/** If the view is visible or not, default: true */
visible?: boolean
/** Views take over the render loop, optional render index (1 by default) */
index?: number
/** If you know your view is always at the same place set this to 1 to avoid needless getBoundingClientRect overhead */
frames?: number
/** The scene to render, if you leave this undefined it will render the default scene */
children?: React.ReactNode
/** The tracking element, the view will be cut according to its whereabouts
* @deprecated You can use inline Views now, see: https://github.com/pmndrs/drei/pull/1784
*/
track?: React.RefObject<HTMLElement>
}
export type ViewportProps = { Port: () => React.ReactNode } & React.ForwardRefExoticComponent<
ViewProps & React.RefAttributes<HTMLElement | THREE.Group>
>
You can define as many views as you like, directly mix them into your dom graph, right where you want them to appear. View is an unstyled HTML DOM element (by default a div, and it takes the same properties as one). Use View.Port inside the canvas to output them. The canvas should ideally fill the entire screen with absolute positioning, underneath HTML or on top of it, as you prefer.
return (
<main ref={container}>
<h1>Html content here</h1>
<View style={{ width: 200, height: 200 }}>
<mesh geometry={foo} />
<OrbitControls />
</View>
<View className="canvas-view">
<mesh geometry={bar} />
<CameraControls />
</View>
<Canvas eventSource={container}>
<View.Port />
</Canvas>
</main>
)